LIQUID BIOPSY
Cancer is the second cause of death, accounting for nearly 9 million deaths in 2017 all over the world. In 2019, 1,762,450 new cancer cases and 606,880 cancer deaths are projected to occur in the United States. It is estimated that metastasis is the primary cause of 90% of all cancer-related deaths. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) detection and analysis are the foundation of non-invasive tests that can be used repeatedly to support early detection, prognosis, theranostic and personal response monitoring to treatment.
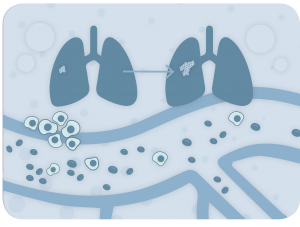
In order to successfully complete the metastatic cascade, cancer cells must:
- detach from the primary tumor
- intravasate into the circulatory system
- elude the immune system control
- extravasate at distant vascular beds
- invade and proliferate in distant organs
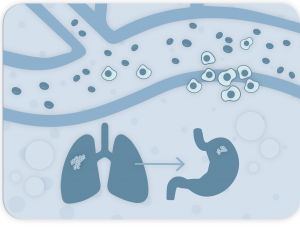
Therefore, Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) represent a powerful tool for:
- study of the invasive potential of a cancer
- early cancer detection
- non-invasive theranostic
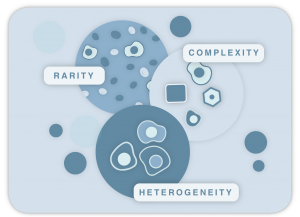
- Circulating Tumor Cells are rare and heterogeneous. They modify their membrane surface properties (Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition, EMT) to enter into the bloodstream. CTCs also have to adapt to escape immune control system.
- Isolation methods based on epithelial surface markers-specific antibodies to capture CTCs can miss cells such as cells going through EMT and may not be suitable for all cancer types.
Not all epithelial cells circulating in the blood are tumor cells since the cells of the different organs can desquamate and end up in the bloodstream.
- Isolation methods must collect circulating cells while keeping intact their morphology and their DNA. They must be compatible with downstream analysis, from morphological analysis to DNA mutation analysis, thus insuring precise characterization of CTCs.

- CTCs are the source of “real-time” information of gene and protein mutations of the tumors.
- CTCs combined with circulating free DNA (cfDNA) may provide a comprehensive understanding of patient’s cancer dynamics.
- Methods collecting CTCs and cfDNA from the same blood draw will ensure efficient access to these critical sources of information.